View basket (0 items $0.00)

Yoga May Prevent Degenerative Disc Disease
The effects of yoga in preventing or eliminating low back pain are well documented. The study below shows that yoga may even reduce degenerative disc disease in the spine, a condition thought to be the precursor of numberous back pain conditions.
A groundbreaking study conducted in Taiwan and published in the European Health Journal in March of 2011 compared the spines of long-time (10 years or more) yoga teachers versus a group of non-yoga practitioners using MRI imaging. The yoga teachers were found to have significantly less degenerative disc disease.
An estimated 80 percent of the population will suffer from back pain at one point in their lives. Back pain is the second most common reason for visits to the doctor, second only to the common cold. The new study is particularly significant because while there are many different diagnoses for back pain, numerous back pain conditions are preceded by degenerative disc disease. Over time, imperceptible degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs can lead to numerous diagnosable conditions.
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) involves disc conditions like bulging or ruptured (herniated) discs. It is also a contributing factor to many other severe back conditions, which afflict people as they get older, including osteoarthritis of the spine, facet joint disorders, and spinal stenosis—a painful and sometimes debilitating condition that involves a narrowing of the spinal canal. 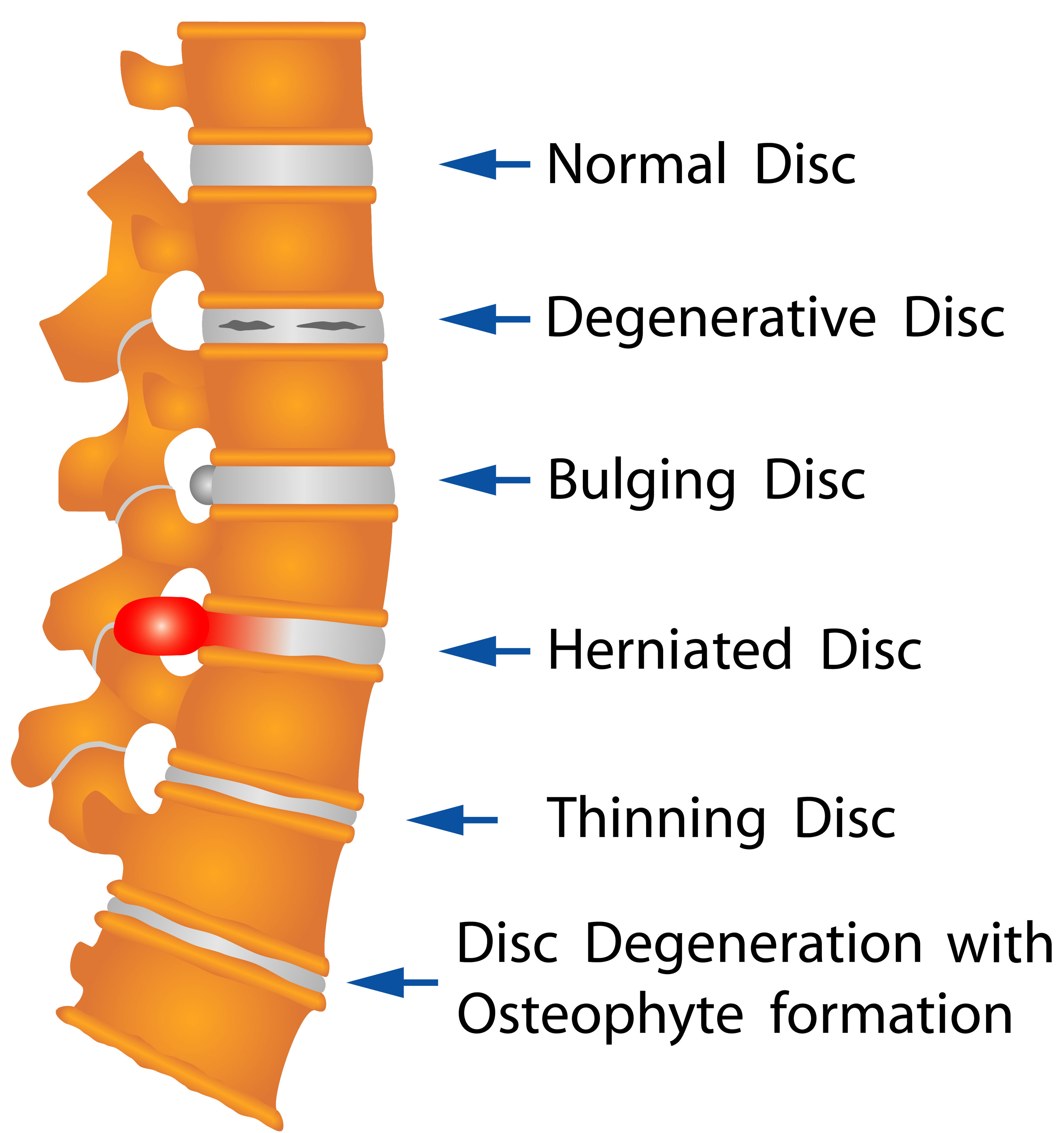
If you’ve never had a disc problem, you might presume that degenerative disc disease is not an issue for you. Unfortunately, chances are that is not the case. The asymptomatic, degenerative changes associated with DDD are much more common than most people realize. MRI studies of healthy people without any symptoms of back problems have found that among people ages 20 to 39, one in three showed degenerative changes of the lumbar spine. In people ages 39 to 60, that number increased to almost six out of ten, or 57 percent. In people aged 60 to 80 years, almost eight out of ten—79 percent—showed some degree of disc degeneration in at least one disc.
Like osteoporosis, disc degeneration is a progressive, degenerative condition that worsens with age. The more advanced the disc deterioration, the greater the chance that problems will spread to other parts of the spine. DDD is so common, in fact, that most doctors hold that it is a “natural part of aging.” Well, so was osteoporosis until it was discovered that bone strength is strongly related to muscle strength. Similarly, there are things that you can do to stay among those 21 percent of 60- to 80-year-olds that did not show any degenerative changes.

In the Taiwanese study, the yoga teachers selected for the study all practiced a gentle and slow form of yoga. As a group, they proved to have significantly less spinal degeneration than the group of control subjects, who were matched for age, sex, and general health and were non-smokers. Interestingly, yoga teachers had better DDD outcomes in the cervical area than the lumbar, though better than non-yoga teachers in both.
The Taiwanese researchers suggested that Hatha yoga may have slowed the natural aging process in intervertebral discs. They speculated that this was due to the stretching and positioning of the spine and the decreased weight-bearing during yoga practice, which all add up to increasing the ability of nutrients to diffuse into the disc.
According to Taiwanese researchers, Hatha yoga may be of significant interest to preventative medicine. While many studies have shown that yoga can reduce back pain, all participants in this study were free of back pain and had no history of heavy lifting. This study showed that long-term yoga practice could prevent several conditions otherwise lying at the root of chronic back pain as people get older.
Featured Courses








